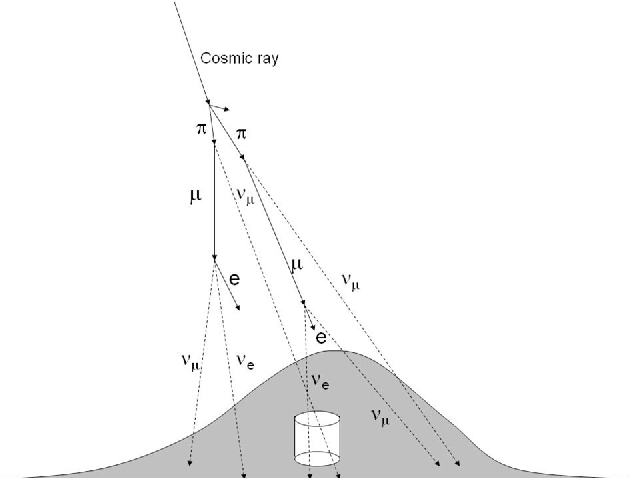
Cosmic rays (protons or nuclei) interact in the upper atmosphere of the Earth. The resulting pions and kaons decay into muons and muon-neutrinos, many of the muons then decay into electrons and a muon-neutrino electron-neutrino pair. All these neutrinos are called atmospheric neutrinos and have been predicted and described in the early 60’s (Markov, Greisen, Reines, Zatsepin,…) [Mar60,Rei60,Gre60]. A crude estimation is that there are two times more muon-neutrinos than electron-neutrinos. In 1965, these atmospheric neutrinos were first detected by two experiments, installed in deep mines in India (Kolar Gold) [Ach65b] and in South Africa [Rei65b].
Interest on these neutrinos renewed in the early 80’s with the building of large underground detectors for the observation of the proton decay which was then predicted by the grand unified theories. Indeed atmospheric neutrino interactions were a background for the rare signal expected from the proton decay. At the end of the 80’s, the first results of the Cerenkov detectors Kamiokande [Hir88] and IMB [Cas91] were showing a small deficit of muon-neutrinos coming from the antipodes. On the contrary, fine resolution tracking detectors like Frejus [Ber90] or NUSEX [Agl89], found results in agreement with the predictions of atmospheric neutrino models [Bar88], though with a limited statistics. The deficit was not statistically convincing and the way to separate the muons and the electrons in Cerenkov detectors was seriously discussed. The muon-neutrino deficit could be interpreted in terms of neutrino oscillation, but such an announcement was clearly too premature (as soon as 1984, at the Neutrino’84 Conference [Kle84], there was a talk by John Learned entitled : « Search for oscillations with atmospheric neutrinos », but no written version…).
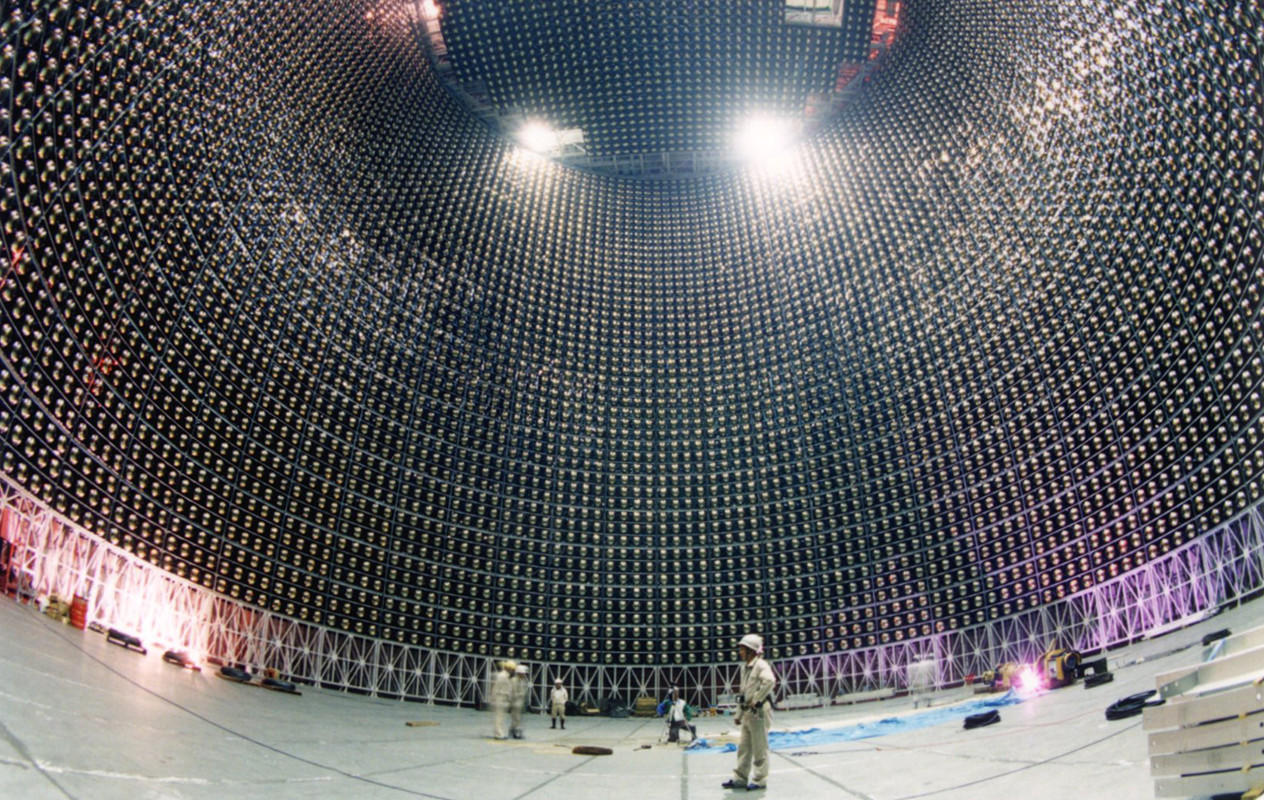

The debate has been solved by the SuperKamiokande experiment that started in 1996. After two years of data taking, SuperKamiokande announced in June 1998 the clear observation of a deficit of muon-neutrinos coming from the antipodes [Fuk98b]; this deficit has been almost immediately interpreted as an oscillation between muon-neutrino and tau-neutrino.
At the same time, the calorimetric MACRO [Amb98] and Soudan 2 [All97] experiments had observed the atmospheric neutrino anomaly, but with a statistical significance insufficient to claim that neutrinos would oscillate.
The oscillation between νμ and ντ has been confirmed by the K2K long-baseline experiment [Ali05].
Calculations of the atmospheric neutrino fluxes have been refined with time. A complete review is in [Gai02].
Further information
During the conference on the History of the Neutrino (Sept. 5-7, 2018 in Paris) the Atmospheric Neutrinos were reviewed by :
- Paolo Lipari (INFN Roma, Italy) (from the pioneering experiments to Kamiokande) and John Learned (University of Hawaii, USA) (the saga of atmospheric neutrinos) : here the video of their talks with the contribution to the Proceedings of P. Lipari and the contribution of J. Learned.
- Takaaki Kajita (University of Tokyo, Japan) describing how the anomaly becomes the discovery : here the slides , the video of his talk and his contribution to the Proceedings.
- and John LoSecco (University of Notre Dame du Lac, USA) presented a poster on the discovery of the atmospheric neutrino anomaly with a written contribution to the Proceedings.
- and Francesco Ronga (INFN Frascaty, Italy) presented a poster on MACRO and the study of neutrino oscillations with a written contribution to the Proceedings.
References
| Author(s) | Title | Reference | Key-words | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ach65a | G.V. Achar et al. | The Kolar Gold Field neutrino experiment | Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays, 1965, Vol. 1, p. 1012 | historical atmospheric atmosbib |
| Ach65b | G.V. Achar et al. | Detection of muons produced by cosmic ray neutrinos deep underground | Phys. Lett. 18 (1965) 196 | historical atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib |
| Agl89 | M. Aglietta et al., NUSEX collaboration | Experimental study of atmospheric neutrino flux in the NUSEX experiment | Europhys. Lett. 8 (1989) 611 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Ali05 | E. Aliu et al., K2K collaboration | Evidence for muon-neutrino oscillation in an accelerator-based experiment | Phys. Rev. Lett. 94 (2005) 081802; arXiv:hep-ex/0411038 | atmospheric accelerator oscillation atmosbib |
| All97 | W.W.M. Allison et al. | Measurement of the atmospheric neutrino flavour composition in Soudan 2 | Phys. Lett. B391 (1997) 491 ; arXiv:hep-ex//9611007 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Amb98 | M. Ambrosio et al., MACRO collaboration | Measurement of the atmospheric neutrino-induced upgoing muon flux using MACRO | Phys. Lett. B434 (1998) 451 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Ash04 | Y. Ashie et al., Super-Kamiokande collaboration | Evidence for an oscillatory signature in atmospheric neutrino oscillations | Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 (2004) 101801 | historical atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib oscbib plotbib |
| Bar88 | S. Barr, T.K. Gaisser, P. Lipari, S. Tilav | Ratio of electron-neutrino/muon-neutrino in atmospheric neutrinos | Phys. Lett. B214 (1988) 147 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Bec92 | R. Becker-Szendy et al., IMB collaboration | A search for muon-neutrino oscillations with the IMB detector | Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 (1992) 1010 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Bec92 | K.S. Hirata et al. , Kamiokande collaboration | Observation of a small atmospheric muon-neutrino/electron neutrino ratio in Kamiokande | Phys. Lett. B280 (1992) 146 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Ber90 | Ch. Berger et al. | A study of atmospheric neutrino oscillations in the Fréjus experiment | Phys. Lett. B245 (1990) 305 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Cas91 | D. Casper et al. | Measurement of the atmospheric neutrino composition with the IMB-3 detector | Phys. Rev. Lett. 66 (1991) 2561 | atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib |
| Cro78 | M.F. Crouch et al. | Cosmic ray muon fluxes deep underground: intensity versus depth and the neutrino induced component | Phys. Rev. D18 (1978) 2239 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Fuk98b | Y. Fukuda et al., Super-Kamiokande collaboration | Evidence for oscillation of atmospheric neutrinos | Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 (1998) 1562 | historical atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib oscbib plotbib |
| Gai02 | T.K. Gaisser and M. Honda | Flux of atmospheric neutrinos | Ann. Rev. of Nucl. and Part. Science 52 (2002) 153 | review annualrev atmospheric atmosbib |
| Gai83 | T.K. Gaisser, T. Stanev, S.A. Bludman and H.S. Lee | The flux of atmospheric neutrinos | Phys. Rev. Lett. 51 (1983) 223 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Gre60 | Kenneth Greisen | Cosmic ray showers | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Sci. 10 (1960) 63 - “Fanciful though this proposal seems, we suspect that within the next decade, cosmic ray neutrino detection will become one of the tools of physics and astronomy” | review annualrev atmospheric atmosbib |
| Hai86 | T.J. Haines et al. | Calculation of atmospheric neutrino induced backgrounds in a nucleon decay search | Phys. Rev. Lett. 57 (1986) 1986 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Hir88 | K.S. Hirata et al., Kamiokande collaboration | Experimental study of the atmospheric neutrino flux | Phys. Lett. B205 (1988) 416 | atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib |
| Hon90 | M. Honda, K. Kasahara, K. Hidaka and S. Midorikawa | Atmospheric neutrino fluxes | Phys. Lett. B248 (1990) 193 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Kaj98 | Takaaki Kajita | Atmospheric neutrino results from Super-Kamiokande and Kamiokande - Evidence for muon-neutrino oscillations | Nucl. Phys. B (Proc. Suppl.) 77 (1999) 123 | historical atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib oscbib plotbib |
| Kle84 | K. Kleinknecht, E.A. Paschos, ed. | XI International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics - Neutrino 84 - Nordkirchen - Dortmund | World Scientific | conference proceedings neutrinoconf atmosbib |
| Kri71 | M.R. Krishnaswamy et al. | The Kolar Gold Field neutrino experiment. 1. The interaction of cosmic ray neutrinos | Proc. Roy. Soc. (A) 323 (1971) 489 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Lea88 | J.G. Learned, S. Pakvasa and T.J. Weiler | Neutrino Mass and Mixing Implied by Underground Deficit of Low-Energy Muon-neutrino Events | Phys. Lett. B207 (1988) 79 | atmospheric atmosbib oscbib |
| Lee63 | T.D. Lee, H. Robinson, M. Schwartz and R. Cool | Intensity of upward muon flux due to cosmic ray neutrinos produced in the atmosphere | Phys. Rev. 132 (1963) 1297 | historical atmospheric atmosbib |
| Lee90 | H. Lee and Y.S. Koh | A new calculation of atmospheric neutrino flux | Nuovo Cimento B105 (1990) 883 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Mar60 | M.A. Markov | On high energy neutrino physics | Proc. 10th Int. Conf. on High-Energy Physics, Rochester, 1960, p. 579 | historical vhe milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib vhebib |
| Men63 | M.G. Menon et al. | On the possibility of experiments with natural neutrinos deep underground | Phys. Lett. 5 (1963) 272; also Nuovo Cimento 30 (1963) 1208 | historical atmospheric atmosbib |
| Nak86 | M. Nakahata et al., Kamiokande collaboration | Atmospheric neutrino background and pion nuclear effect for Kamioka Nucleon Decay experiment | J. Phys. Soc. Jap. 55 (1986) 3786 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Rei60 | Frederick Reines | Neutrino interactions | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Sci. 10 (1960) 1 | review annualrev properties atmosbib |
| Rei65b | F. Reines, M.F. Crouch, T.L. Jenkins, W.R. Kropp, H.S. Gurr, G.R. Schmid, J.P.F. Sellschop, B. Meyer | Evidence for high energy cosmic ray neutrino interactions | Phys. Rev. Lett. 15 (1965) 429 | historical atmospheric milestonebib overviewbib atmosbib vhebib |
| Rei71 | F. Reines et al. | Muons produced by atmospheric neutrinos: Experiment | Phys. Rev. D4 (1971) 80 and Phys. Rev. D4 (1971) 99 | atmospheric atmosbib |
| Zat62 | G.T. Zatsepin and V.A. Kuzmin | Neutrino production in the atmosphere | Sov. Phys. JETP 14 (1962) 1294 | historical atmospheric atmosbib |
