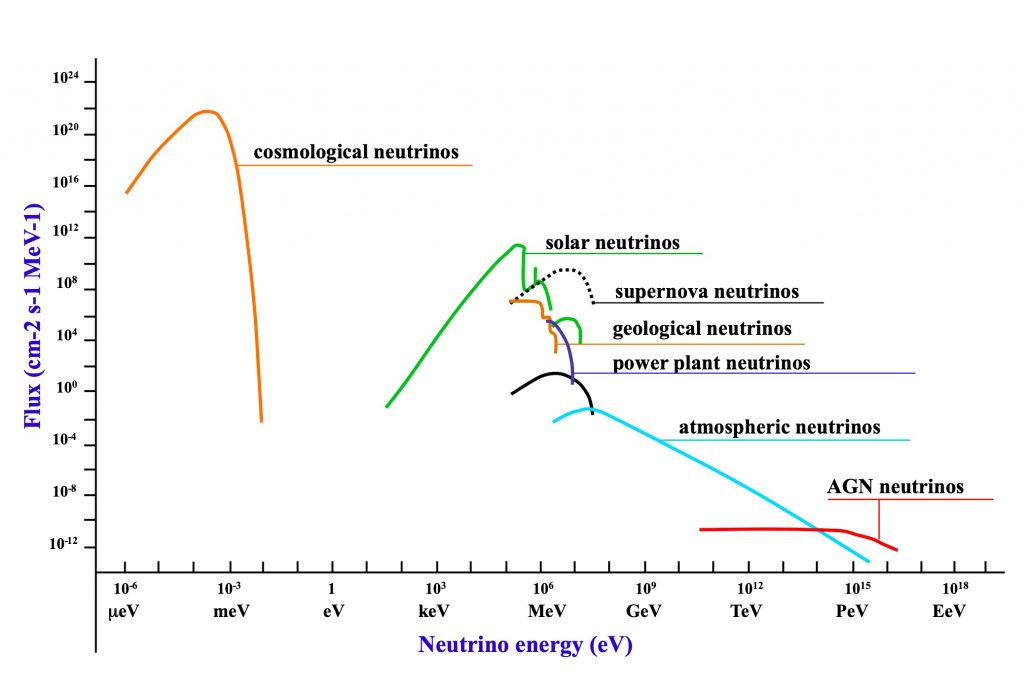
There are many neutrino sources in the Universe, either astrophysical or terrestrial, observed in many different processes. The first Grand Unified Neutrino Spectrum (neutrino flux versus neutrino energy, such named recently in [Vit19]) appeared first in 1995 in the book “La lumière des neutrinos” (in French) [Cri95]. It has been reproduced in several proceedings of conferences (see for example [Spi99]). It has been quoted by W. Haxton et al. who calculated the thermal flux of low-energy solar neutrinos [Hax00].
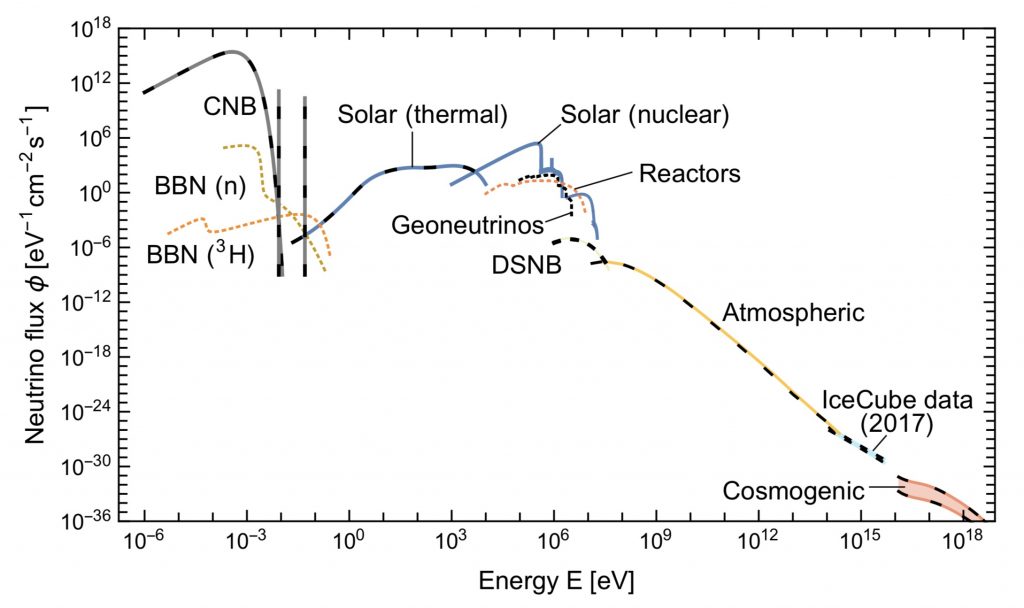
In [Vit19] G. Raffelt and collaborators revisited in great detail the different components in the light of the new discoveries and published this new version of the Grand Unified Neutrino Spectrum, much more precise quantitatively. CNB is for cosmic neutrino background, BBN for big bang nucleosynthesis, DSNB for diffuse supernova neutrino background, cosmogenic for neutrinos coming from the interaction of ultra high-energy cosmic-rays with the cosmic microwave background CMB.
References
| Author(s) | Title | Reference | Key-words | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cri95 | Michel Cribier, Michel Spiro, Daniel Vignaud | La lumière des neutrinos | Seuil (1995) | book outreach neutrinosrc |
| Hax00 | W.C. Haxton and W. Lin | The very low energy solar flux of electrons and heavy-flavor neutrinos and antineutrinos | Phys. Lett. B486 (2000) 263 ; arXiv:nucl-th/0006055 | solar neutrinosrc |
| Spi12 | Christian Spiering | Towards High Energy Neutrino Astronomy – A Historical Review | European Physical Journal H 37 (2012) 515; arXiv:1207.4952 | history vhe vhebib neutrinosrc |
| Spi99 | M. Spiro, D. Vignaud | Neutrino physics and astrophysics | Nucl. Phys. A654 (1999) 350c | review neutrinosrc |
| Vit19 | E. Vitagliano, I. Tamborra, G. Raffelt | Grand unified neutrino spectrum at Earth | Rev. Mod. Phys. 92 (2020) 45006; arXiv:1910.11878 | rmp neutrinosrc |
